Introduction
Chikungunya is a mosquito-borne viral disease that has been creating waves of concern across various regions of the world. In recent months, Karachi, the largest city in Pakistan, has seen a noticeable increase in Chikungunya cases, sparking concerns about the city’s healthcare readiness and mosquito control measures. This article delves deep into the current situation of Chikungunya cases on the rise in Karachi, its causes, symptoms, and preventive measures.

What is Chikungunya?
Humans contract chikungunya from infected mosquitoes, especially those of the Aedes aegypti and Aedes albopictus species. Originating in Africa, the disease has spread throughout the world, infecting millions of individuals in tropical and subtropical areas.
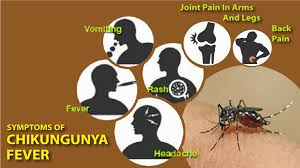
Symptoms of Chikungunya
The primary symptoms of Chikungunya include:
- High fever
- Severe joint pain
- Muscle pain
- Headache
- Fatigue
- Rash
These symptoms usually appear 4-7 days after being bitten by an infected mosquito. While Chikungunya is rarely fatal, the joint pain can be debilitating and last for months or even years.
Chikungunya Cases in Karachi: The Alarming Rise
The recent uptick in Chikungunya cases in Karachi is worrying. Various factors have contributed to this rise, including climatic conditions, inadequate sanitation, and poor mosquito control measures. According to local health authorities, the number of reported cases has doubled compared to the previous year, signaling the need for immediate intervention.
Causes Behind the Surge in Chikungunya Cases in Karachi
Several reasons have been identified for the increase in Chikungunya cases in Karachi:
- Monsoon Season: The onset of the monsoon season creates ideal breeding conditions for mosquitoes, with stagnant water accumulating in various parts of the city.
- Lack of Effective Mosquito Control: Karachi’s municipal services have struggled to maintain effective mosquito control programs, leading to a rise in the mosquito population.
- Urbanization and Overcrowding: The city’s rapidly growing population and urbanization have contributed to unsanitary conditions, making it easier for mosquito-borne diseases to spread.
- Climate Change: Rising temperatures and changing weather patterns have extended the breeding season for mosquitoes, increasing the risk of outbreaks.
How Chikungunya is Spread
When a mosquito attacks someone who has already contracted the illness and then bites someone else, it can spread the Chikungunya virus. Direct human-to-person transmission of the virus is not possible. Generally speaking, during the day, especially in the early morning and late afternoon, Chikungunya-carrying mosquitoes are active.
Prevention and Control of Chikungunya
A multimodal strategy is needed to prevent Chikungunya, with a focus on bite avoidance and mosquito population reduction. Among the most successful techniques are:
Removing standing water from drains, containers, and other places where mosquitoes breed is one way to eliminate breeding sites.
Applying DEET, picaridin, or oil of lemon eucalyptus-containing insect repellent to exposed skin is how to use them.
Wearing Protective Clothes: To reduce skin exposure, put on long sleeve shirts and pants.
Installing Mosquito Nets: To keep mosquitoes out of homes, use window screens and bed nets.
The application of insecticides on a regular basis is recommended in places where mosquitoes are likely to develop, particularly during the rainy season.

Symptoms and Diagnosis of Chikungunya
Chikungunya is often mistaken for dengue fever due to the similarity in symptoms, such as fever and joint pain. However, Chikungunya is characterized by its intense joint pain, which can persist for months. Diagnosis is usually confirmed through a blood test that detects the presence of Chikungunya antibodies.
Treatment for Chikungunya
For Chikungunya, there isn't a specific antiviral medication. The main goals of the disease's management are to reduce the pain and fever. Typical therapeutic approaches consist of:
Pain Relief: Ibuprofen and paracetamol, two over-the-counter pain medications, can help lower temperature and joint pain.
Rest and Hydration: In order to stay hydrated, patients are encouraged to rest and consume a lot of fluids.
Physical Therapy: To help relieve joint pain and stiffness, physical therapy may be suggested in certain situations.
Impact of Chikungunya on Karachi’s Healthcare System
The local administration has started a number of initiatives to contain the Chikungunya outbreak, such as:
Programs for controlling mosquitoes: stepping up efforts to get rid of mosquito breeding grounds and applying pesticides where they are affected.
population awareness campaigns: teaching the general population how to avoid mosquito bites and identify the disease's signs.
Improving Healthcare Services: Enhancing healthcare facilities to meet the increased number of Chikungunya patients and offer prompt treatment.
Global Perspective on Chikungunya
Chikungunya is a worldwide health hazard, not just in Karachi, Pakistan. In recent years, outbreaks have been reported in countries in Africa, Asia, and the Americas. Through concerted efforts, international health agencies, such as the World Health Organization (WHO), have been trying to monitor and control the disease's spread.
The Role of Climate Change in the Spread of Chikungunya
Climate change has played a significant role in the spread of Chikungunya. Warmer temperatures have expanded the habitats of mosquitoes, allowing them to thrive in areas that were previously unsuitable for their survival. This has led to the spread of Chikungunya to new regions, including parts of Europe and the Americas.
Chikungunya vs. Dengue: Understanding the Differences
Dengue and chikungunya are mosquito-borne illnesses, but they are caused by different viruses and exhibit different symptoms. Dengue generally leads to more severe consequences, including hemorrhagic fever, whereas Chikungunya is renowned for causing persistent joint pain. Correct diagnosis and management of the two diseases depend on an understanding of their distinctions.
FAQs
What is the main cause of Chikungunya?
Chikungunya is caused by a virus transmitted through the bite of infected mosquitoes, primarily Aedes aegypti and Aedes albopictus.
2. How can I prevent Chikungunya?
Prevent Chikungunya by eliminating mosquito breeding sites, using insect repellent, wearing protective clothing, and using mosquito nets.
3. Is there a cure for Chikungunya?
There is no cure for Chikungunya, but the symptoms can be managed with pain relievers, rest, and hydration.
4. How long do Chikungunya symptoms last?
Symptoms of Chikungunya typically last for 1-2 weeks, but joint pain can persist for months or even years.
5. Can Chikungunya be fatal?
Chikungunya is rarely fatal, but it can cause severe joint pain and discomfort that may last for a long time.
6. What should I do if I suspect I have Chikungunya?
If you suspect you have Chikungunya, seek medical attention immediately. A blood test can confirm the diagnosis, and your doctor can recommend appropriate treatment.
Conclusion
There is an urgent need to address the serious public health concern posed by the increase of Chikungunya cases in Karachi. Although the illness rarely poses a threat to life, it can nevertheless result in excruciating pain and persistent symptoms. The implementation of preventive measures, prompt diagnosis, and treatment are essential for managing the transmission of Chikungunya and reducing its adverse effects on the populace.








